Cold-Rolled Steel vs. Hot-Rolled Steel: Understand the Differences in One Article!
Do you always get confused between cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel when selecting materials? Today, we'll guide you step by step to clearly distinguish these two types of steel !
In this article, we will cover:
* The differences in production processes between cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel
* A comparison of the performance characteristics of both steels
* Industry-specific application scenarios, price differences, and tips for visual identification
· Production Process
Hot-Rolled Steel: Softened at temperatures above 1000°C, then rough-rolled and finished-rolled.
Cold-Rolled Steel: Hot-rolled coils are pickled and then processed through multiple cold-rolling passes at room temperature.
· Performance Comparison
Strength: Cold-rolled steel has higher strength but lower toughness; hot-rolled steel offers better ductility and impact resistance.
Surface: Cold-rolled steel has a smooth, mirror-like finish; hot-rolled steel has an oxide layer giving it a sandpaper-like texture.
Thickness: Cold-rolled steel mainly covers thin gauges (0.2–2.0 mm), while hot-rolled steel is used for thicker sections (above 4.0 mm).
· Application Scenarios
Automotive Manufacturing: DC03 cold-rolled steel achieves 0.1 mm-level stamping precision. Jin Steel Holdings’ cold-rolled steel replaces imported materials, improving utilization by 25%.
Construction Engineering: Q345B hot-rolled steel for stadiums has stood the test of 15 years without tearing. X80 hot-rolled pipes for cross-sea bridges withstand pressures at 50 meters below sea level.
Home Appliances: Refrigerator outer panels use 0.6 mm cold-rolled steel passing 1,000-hour salt spray tests, while internal brackets use 4.0 mm hot-rolled steel supporting 300 kg.
· Cost Analysis
The price difference mainly arises from additional processes such as pickling and annealing.
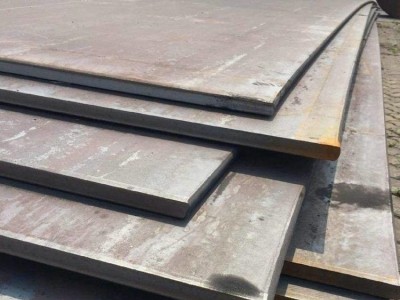

· Identification Methods
1️⃣ Visual Inspection:
Cold-rolled steel has a silver-white, mirror-like surface, while hot-rolled steel appears dark brown with a rusty tone.
2️⃣ Edge Touch Test:
Cold-rolled steel has smooth, clean-cut edges at approximately a 45° angle, whereas hot-rolled steel edges typically have burrs of about 0.5–1.0 mm.
3️⃣ Thickness Measurement:
Common thicknesses for cold-rolled steel are 0.2 / 0.3 / 0.5 / 0.8 / 1.0 / 1.2 / 1.5 / 2.0 mm.
Hot-rolled steel is mainly supplied in 4.0 / 5.0 / 6.0 mm thicknesses (in accordance with national standards).
· Purchasing Guide
Choose cold-rolled steel for applications requiring high precision, superior surface finish, or small-batch production.
Choose hot-rolled steel for applications demanding toughness, structural strength, or large-scale engineering projects.
Pickled and oiled hot-rolled steel offers a balanced option, combining solid performance with good cost efficiency, and can serve as an effective alternative.